If you are looking for BESC-134 IGNOU Solved Assignment solution for the subject Education as a Practice, you have come to the right place. BESC-134 solution on this page applies to 2023-24 session students studying in BAG courses of IGNOU.
BESC-134 Solved Assignment Solution by Gyaniversity
Assignment Code: BESC-134 /TMA / July 2023 and January 2024
Course Code: BESC-134
Assignment Name: Education as a Practice
Year: 2023-2024
Verification Status: Verified by Professor
Assignment A
Answer the following in about 500 words each.
Q1) Describe the main characteristics of action research. Explain the basic steps in which action research can be accomplished?
Ans) Characteristics of action research are the following:
Borgia and Schuler (1996) emphasize the 'Five Cs'—Commitment, Collaboration, Concern, Consideration, and Change—in action research:
a) Commitment: This is the first characteristic, focusing on the time participants need to build trust, observe practices, and reflect on results. Commitment is essential for conducting effective research.
b) Collaboration: In action research, each person contributes with equal power relations among participants. It involves a cyclic process of sharing, giving, and taking.
c) Concern: Trust in each other and the value of the study/task is crucial. Participants should develop support from critical stakeholders.
d) Consideration: Consideration involves a challenging assessment of one's behaviour, requiring concentration and care as patterns and relationships are sought for meaningful investigation.
e) Change: Change is ongoing and challenging but vital to remain an effective teacher. It signifies the adaptability and improvement inherent in action research.
Additional Characteristics:
a) Clear Vision: Action research enables teachers to have a clear vision of complex social situations in a classroom or school, facilitating problem-solving.
b) Stakeholder Support: Collaboration with stakeholders is evident, highlighting the importance of understanding the situation and teamwork.
c) Reflective Practice: Pondering on issues from different angles and reflection is an essential feature of action research.
d) Focus on Teaching-Learning Improvement: The primary focus is on improving the teaching-learning situation in a specific context.
e) Systematic and Specific: It follows systematic steps like any research but is highly specific to a particular class, school, or situation, with findings not generalized.
f) Continuous Learning: Action research encourages teachers to engage in intellectual pursuits, fostering continuous learning and professional development.
g) Planning and Restructuring: Action research commonly contributes to planning and restructuring existing education systems.
h) Narrowly Focused: It is narrowly focused research, typically undertaken by teachers and practitioners in a specific situation.
i) Contextual: Action research is contextual, performed for a certain specific context.
j) Steps in Action Research:
k) Research is a systematic process, and action research, a specific type, involves several steps that teachers can follow:
l) Identify a Problem: Teachers initiate action research by identifying a problem within their teaching context. This can involve collecting information about classroom events, incidents, or specific subjects through various methods such as observation, interviews, questionnaires, or lesson recordings.
m) Specify the Problem: After identifying the problem, the next step is to specify and detail it. This involves pinpointing the research question or issue clearly, providing a focused direction for the investigation.
n) List Probable Causes: Teachers then list all possible causes contributing to the identified problem. This step requires a comprehensive examination of potential factors behind the issue. It involves taking note of all the reasons that might be working behind the problem.
o) Hypothesizing: Once the causes are listed, the teacher selects one as the most potent and formulates a hypothesis. This involves looking for probable solutions or a tentative hunch to address the problem. The hypothesis guides the subsequent actions in the research.
p) Action Plan: Following the formulation of a hypothesis, a detailed action plan is developed. This plan outlines the tasks to be undertaken, the strategy to be adopted, the execution process, and the recording of evidence. It also includes considerations of the time required to complete the study and the resources needed for the task. This detailed planning contributes to the effectiveness of the research process.
q) Interpretation of Results: The final step involves interpreting the results based on the executed action plan. The teacher or investigator writes conclusions derived from the research, reflecting on the effectiveness of the implemented actions. This step helps in understanding the impact of the undertaken strategies and whether they addressed the identified problem.
Q2) Describe the need of research for improving educational practices. Explain how ‘case-studies’ help does in improving learning and teaching. Give suitable examples.
Ans) Every society undergoes revolutions, discoveries, and inventions crucial for its sustainability and progress. In the realm of education, constitutional provisions, global agendas like UNESCO's Sustainable Development Goal-2030, the Rights of People with Disabilities (RPWD) Act, 2016, and the National Education Policy-2020 set new targets, impacting the educational landscape. The unprecedented challenges posed by the Covid-19 pandemic have further necessitated adjustments in the teaching-learning system globally.
In addressing the evolving educational landscape, research plays a pivotal role:
a) Enhancing Knowledge: Educational research contributes to expanding the knowledge base by introducing new theories and concepts, providing meaningful and socially acceptable explanations for knowledge creation.
b) Understanding Learners and Their Needs: Researchers focus on learners' development, psychological, social, and educational needs, individual differences, learning pace, and styles, as well as their attitudes, interests, and aspirations.
c) Comprehending Disciplines and Subjects: Research delves into understanding disciplinary knowledge, exploring how disciplines grow, establish distinct features, and contribute to the overall educational landscape.
d) Establishing Effectiveness of Methods and Strategies: Research evaluates the effectiveness of various educational methods, strategies, and instructional designs through experimental and comparative studies, providing insights into what works best in different educational contexts.
e) Solutions to Classroom Problems: Action research, often conducted by teachers, aims to find localized solutions to day-to-day classroom challenges. These research endeavours are context-specific, addressing the immediate needs of teachers and practitioners.
f) Examining Assessment Practices: The evolving nature of educational practices demands continuous research on the effectiveness of assessment strategies and tools. Researchers explore new and innovative assessment practices, including technological interventions.
g) Integrating Technologies and Innovations: As technology becomes integral to education, research is crucial in understanding the adoption, impact, and potential of technological interventions. The National Education Policy-2020 emphasizes the need for research in future disruptive technologies.
Case Studies
Case studies, a qualitative research method, serve a dual purpose as both a research tool and a teaching-learning aid. In education and various disciplines such as social sciences, management, psychology, humanities, law, and medicine, case studies are instrumental in cultivating higher-order thinking skills, analytical abilities, and problem-solving skills among learners.
Case Study as a Teaching-Learning Tool:
a) Development of Higher-Order Skills: Case studies, derived from real-life situations and problems, are potent tools for scenario-based education. They contribute to the development of higher-order skills such as critical thinking, analysis, problem-solving, and decision-making.
b) Scenario-Based Learning: Utilizing case studies in teaching involves presenting learners with scenarios based on real events. This approach allows learners to engage with practical, real-world situations, enhancing their understanding and application of theoretical concepts.
c) Versatility Across Disciplines: Case studies are versatile tools applicable across diverse disciplines. Teachers can utilize existing cases or create new ones, ensuring relevance to the subject matter.
d) Encouraging Multiple Perspectives: Learners, when exposed to a case or event, are prompted to think, analyse, explain, and reflect. The same case can be viewed from different perspectives, fostering an appreciation for diverse viewpoints, and encouraging respect for others' opinions.
e) Active Learning Approach: Case studies promote an active learning approach where students are actively involved in the learning process. They are encouraged to participate in discussions, share their insights, and collectively explore potential solutions.
f) Application of Knowledge: The application of theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios is a key aspect of case-based learning. Learners can bridge the gap between theory and application, preparing them for real-world challenges.
Assignment B
Answer the following questions in about 250 words each.
Q3) What is Nali-Kali Project? In what ways it was an innovative project.
Ans) Nali-Kali, initiated in 1995 in Mysore District with UNICEF assistance, aimed to rejuvenate primary education in selected schools. The region faced challenges like student absenteeism due to various factors, including seasonal migration, and traditional teacher-centric pedagogy.
To address these issues, 15 motivated teachers studied innovative pedagogy in Rishi Valley, Andhra Pradesh, and implemented it in Mysore schools. The success led to the statewide adoption of Nali-Kali under the DPEP project. This reform empowered teachers to adopt child-centred pedagogy, especially suitable for multi-grade teaching.
Nali-Kali emphasizes joyful learning, departing from conventional chalk-talk methods. Teaching-learning materials (TLMs) were developed based on principles like 'from known to unknown' and 'concrete to abstract.' Readiness cards, content cards, practice cards, application cards, and evaluation cards were created to attract children and ensure learning.
The curriculum in language, mathematics, and environmental studies was structured into manageable units called 'Milestones' and organized into learning ladders. Each milestone was a step on the ladder, promoting self-learning and reinforcing competencies before progressing.
This approach, distinct from traditional and even DPEP activity-based learning, prioritizes joyful, child-centred education, breaking hierarchical teacher-student dynamics. Nali-Kali goes beyond the formal school system, fostering a transformative shift. The program also introduced tools for evaluation and remedial teaching methods, contributing to a holistic educational experience.
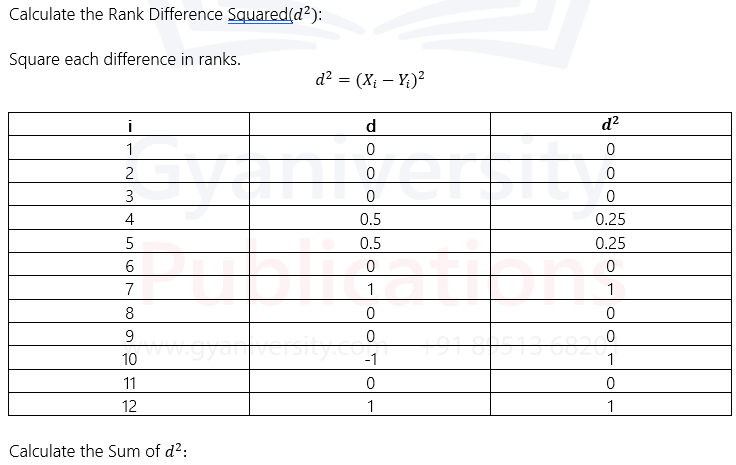
Q4) Compute correlation of the marks of 12 students in rank order method.
Scores (English) : 25, 28, 35, 36, 22, 20, 30, 18, 38, 32, 40, 36
Scores (Social Studies) : 20, 25, 26, 29, 15, 17, 25, 16, 28, 26, 38, 35
Ans) To compute the correlation coefficient using the rank order method, follow these steps:
Rank the Scores:
Rank the scores separately for both subjects, from the lowest to the highest.
English Scores (X): 18, 20, 22, 25, 28, 30, 32, 35, 36, 36, 38, 40
Social Studies Scores (Y): 15, 16, 17, 20, 25, 26, 26, 28, 29, 35, 38, 38
Calculate the Difference in Ranks:
Find the difference between the ranks for each pair of scores.
Q5) Describe the barriers for imparting inclusive education in schools
Ans) The implementation of inclusive education in India faces numerous obstacles despite government prioritization and legislative efforts. Attitudinal barriers, deeply rooted in societal norms, hinder the acceptance and accommodation of children with disabilities.
Discrimination, bullying, and a lack of effort to adapt the curriculum or environment contribute to high dropout rates. Physical barriers, such as inaccessible school structures and facilities, pose challenges for children with disabilities. A rigid curriculum, teacher unwillingness or lack of training, language and communication issues, socio-economic factors, inadequate funding, and policy ambiguities further impede the success of inclusive education.
Societal attitudes, especially regarding disability, create resistance to inclusive education. Teachers often lack the knowledge and skills necessary for effective inclusion, contributing to communication issues, inappropriate management, and neglect of individual needs. The language barrier and socio-economic challenges affect diverse learners, making learning difficult. Funding shortages and policy misunderstandings persist at various levels, impacting the quality of education for children with special needs.
Overcoming these barriers requires rational funding, attitudinal shifts, and policy adjustments. Inclusive education should be integral to teacher education programs, emphasizing sensitivity and responsibility. Practical orientation and resource teacher-led sensitization can improve school environments, teaching strategies, and the overall inclusivity of education. Embracing inclusive education is crucial for promoting equity, realizing constitutional educational rights, and fostering societal change.
Q6) What are the different types of Interviews? What steps will you follow while conducting an interview?
Ans) An interview is a verbal communication, either face-to-face or telephonic, between a researcher and a respondent, where information is shared with the researcher. This method is commonly used in qualitative and descriptive studies to collect data on perceptions, attitudes, opinions, etc. There are two main types of interviews: structured and unstructured.
Structured Interviews: Structured interviews are formal and follow a predetermined sequence and wording. They consist of fixed, closed-ended questions, making them standardized. This approach enhances the reliability and credibility of data. Responses from participants are recorded on a standardized schedule.
Unstructured Interviews: Unstructured interviews encourage subjects to speak freely, fostering rapport building. Initially, few questions are asked, and the researcher can ask questions as needed, following their intuition. This informal method allows flexibility in sequencing and wording, and the researcher can elaborate on or clarify questions during the interview.
Steps in Conducting an Interview:
a) Preparing for the Interview: Clearly define the purpose of the interview and the information needed. Decide on the type of interview (individual or group) and outline the sequence of questions.
b) Conducting the Interview: Establish rapport at the beginning. Ask questions in a planned sequence, avoiding rigidity. Frame questions in a stimulating and encouraging manner. Use a recording device without distracting the interviewee.
c) Recording and Interpreting Responses: Ideally, use a recording device to retain the exact wording of responses. If notes are taken during the interview, ensure they are done simultaneously or immediately afterward.
Assignment C
Answer the following questions in about 125 words each.
Q7) Discuss, how the philosophical principles translated into educational practices?
Ans) Philosophical principles play a pivotal role in shaping educational practices, guiding the development of pedagogical approaches and educational frameworks. For example, in the realm of progressivism, influenced by John Dewey's philosophy, the principle of learning by doing is translated into experiential learning methods.
Similarly, the philosophical belief in the social nature of learning, rooted in constructivism, is manifested in collaborative and interactive teaching strategies. Essentialism, with its emphasis on core knowledge, translates into a structured curriculum focused on foundational subjects.
Pragmatism's practical orientation influences a curriculum designed to meet real-world challenges. Philosophical principles provide the foundational framework that educators draw upon to define curriculum, teaching methods, and the overall educational environment.
Q8) What are the main features of ‘Lok Jumbish Pariyojana’?
Ans) Lok Jumbish Pariyojana, a prominent initiative in India, is characterized by various key features. Firstly, it focuses on universalizing elementary education in rural areas, addressing challenges related to access and retention.
The program emphasizes community participation and involvement in decision-making processes, fostering a sense of ownership. Innovative and child-centric methods, such as Activity-Based Learning (ABL), are integral to Lok Jumbish Pariyojana, aiming to make education more engaging. The initiative also prioritizes teacher training and development to enhance pedagogical practices.
It encourages decentralized planning, with District Education Groups playing a crucial role in local-level implementation. Overall, Lok Jumbish Pariyojana is marked by its integrated approach, combining community engagement, innovative teaching methodologies, and a commitment to universal education in rural India.
100% Verified solved assignments from ₹ 40 written in our own words so that you get the best marks!
Don't have time to write your assignment neatly? Get it written by experts and get free home delivery
Get Guidebooks and Help books to pass your exams easily. Get home delivery or download instantly!
Download IGNOU's official study material combined into a single PDF file absolutely free!
Download latest Assignment Question Papers for free in PDF format at the click of a button!
Download Previous year Question Papers for reference and Exam Preparation for free!